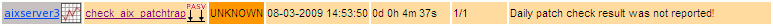Introduction

Despite all inroads made by Linux, commercial UNIX variants such as IBM's AIX
are still used in numbers, especially when the application software stack comes from
the same vendor. Cross-platform migrations can be hard to introduce, even with
clear benefits. Since AIX is running exclusively on IBM's line of CPU's and hardware,
it is harder to get the professional support due to the limited HW availability.
As a result, OS patch management for AIX is lacking and it is a cumbersome manual
process. Generating AIX patch update notifications into our standard Nagios patch
monitoring promises to improve the AIX patch management.
IBM, like all major OS vendors, introduced a web-based online patch update service
that simplifies the process to select and obtain the latest patches.
With AIX 5L Version 5.3, the new "Service Update Management Assistant"
feature SUMA was released to help automate the patching.
Plugin Design with SSH
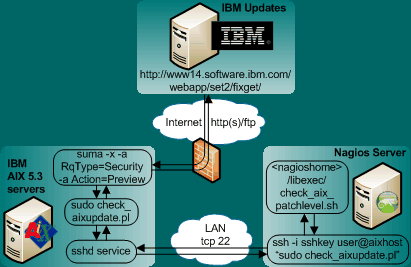
By using the 'suma' command, we can query the IBM update server for applicable patches to our particular OS installation. The settings for this update query can be adjusted to set the usual proxy server parameters to enable access from the intranet. By processing and formatting the query output for Nagios, we can create a plugin that notifies our admins about the latest IBM patches available. It also serves to inform the security and compliance team to about outstanding patches to better judge the systems risk level.
For transporting the list of patch updates back to Nagios, we have 2 different design choices, each with it's own advantages and disadvantages:
- Active, remote plugin command execution using key-based SSH
- Passive, scheduled check result transmission through SNMP traps
Configure and test the 'suma' command on AIX
Running the 'suma' command requires root privileges, so we either need login as root, use 'su' or, if available, use 'sudo'.
$ sudo suma -c
Password:
FIXSERVER_PROTOCOL=http
DOWNLOAD_PROTOCOL=ftp
DL_TIMEOUT_SEC=180
DL_RETRY=1
MAX_CONCURRENT_DOWNLOADS=5
HTTP_PROXY=
HTTPS_PROXY=
FTP_PROXY=
SCREEN_VERBOSE=LVL_INFO
NOTIFY_VERBOSE=LVL_INFO
LOGFILE_VERBOSE=LVL_VERBOSE
MAXLOGSIZE_MB=1
REMOVE_CONFLICTING_UPDATES=yes
REMOVE_DUP_BASE_LEVELS=yes
REMOVE_SUPERSEDE=yes
TMPDIR=/var/suma/tmp
FIXSERVER_URL=www14.software.ibm.com/webapp/set2/fixget
$ sudo suma -c -a HTTP_PROXY=http://192.168.100.184:80/
$ sudo suma -c -a DL_TIMEOUT_SEC=10
$ sudo suma -c |grep HTTP_PROXY
HTTP_PROXY=http://192.168.100.184:80/Now we are able to run a 'suma' query to list the latest patches available. See also 'man suma'. Unless we are already fully patched, we will now receive a list of patch filenames containing the fileset and latest (Version.Release.TL.Fix) patch level (example below). The *.bff file extension stands for (b)ackup (f)ormat (f)ile, IBM's unique file format the patch is delivered in.
$ sudo suma -x -a RqType=Security -a Action=Preview
****************************************
Performing preview download.
****************************************
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/OpenGL.OpenGL_X.dev.vfb.5.3.7.1.bff
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/OpenGL.OpenGL_X.rte.base.5.3.7.1.bff
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/OpenGL.OpenGL_X.rte.soft.5.3.7.1.bff
...
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/sysmgt.websm.apps.5.3.7.1.bff
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/sysmgt.websm.rte.5.3.7.2.bff
Summary:
217 downloaded
0 failed
0 skippedDownload and install the check-aix-update.pl script (for SSH)
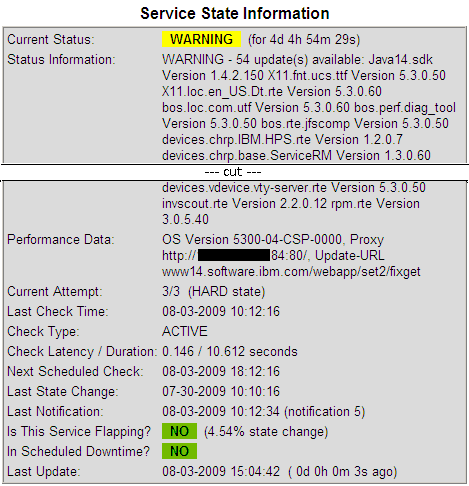
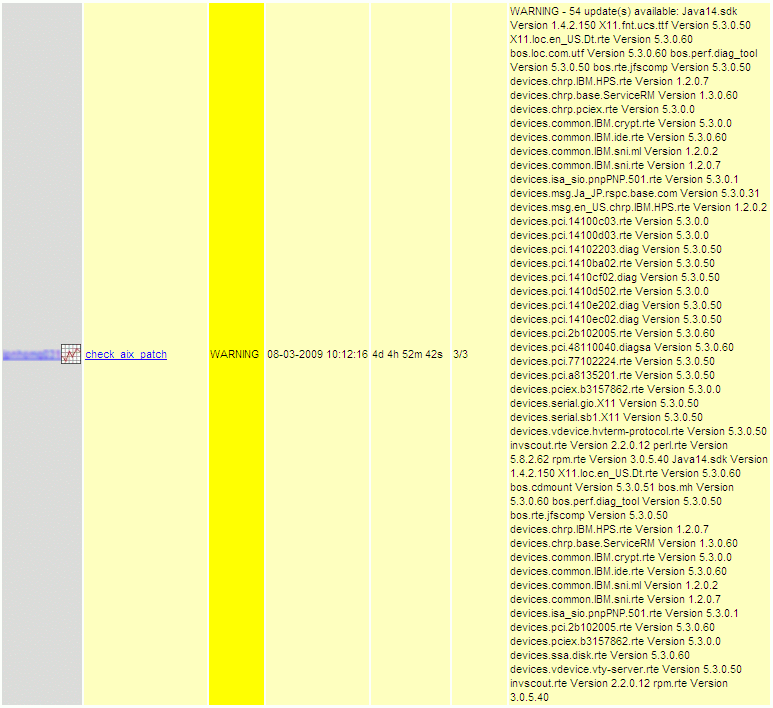
The script check-aix-update.pl was written to run suma, compare the returned list against the list of installed filesets generated with lslpp and format the result to be usable for Nagios. It is to be placed on the AIX server and can be run directly through SSH. By testing it directly on the AIX server, we can see the Nagios output. Note the OS version, proxy setting and update URL that is additionally provided in the performance data section.
$ sudo /scripts/check-aix-update.pl
WARNING - 211 update(s) available: X11.Dt.lib Version 5.3.7.2 X11.Dt.rte Version 5.3.7.3
X11.apps.rte Version 5.3.7.1 X11.base.lib Version 5.3.7.2 X11.base.rte Version 5.3.7.5
bos.64bit Version 5.3.7.7 bos.acct Version 5.3.7.8 bos.adt.base Version 5.3.7.3
bos.adt.debug Version 5.3.7.3 bos.adt.include Version 5.3.7.7 bos.adt.insttools Version
5.3.7.2
...
perfagent.tools Version 5.3.7.4 printers.rte Version 5.3.7.2|OS Version 5300-07-01-0748,
Proxy http://192.168.100.184:80/, Update-URL www14.software.ibm.com/webapp/set2/fixgetPrepare the remote plugin execution through SSH on the Nagios system
Let's talk shortly about the implications of running the update check plugin through SSH. We need to either create a passwordless SSH key or code the password into the Nagios server side configuration in order to allow for the automated plugin check execution. With the need for having root rights to execute the plugin on the remote side, AIX security now starts to depend on the Nagios system. The advantage of this setup is a "active" plugin that can be executed any time through Nagios, giving direct feedback. There is a way to avoid the security implications of the SSH-based plugin execution: using a passive check setup that is triggered on the AIX server itself. More about this further down, first the SSH-based setup:
nagios@susie112:~> ssh-keygen -t dsa -b 2048 -f .ssh/nagios-key
Generating public/private dsa key pair.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in .ssh/nagios-key.
Your public key has been saved in .ssh/nagios-key.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
af:31:12:5a:d1:13:bb:78:56:19:4f:a1:68:89:9d:f3 nagios@susie112
copy .ssh/nagios-key.pub to user@192.168.245.129:/home/user/.ssh/authorized_keys
(chmod to 600 for rw-------)Now we can test the remote plugin execution from the Nagios server:
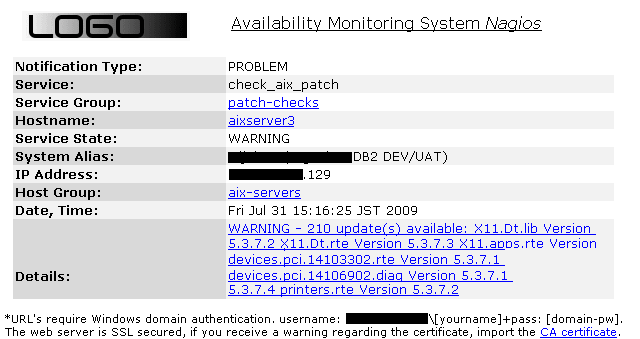
nagios@susie112:~> ssh -i .ssh/nagios-key user@aixserver3 "sudo /scripts/check-aix-update.pl"
WARNING - 210 update(s) available: X11.Dt.lib Version 5.3.7.2 X11.Dt.rte Version 5.3.7.3
X11.apps.rte Version 5.3.7.1 X11.base.lib Version 5.3.7.2 X11.base.rte Version 5.3.7.5
bos.64bit Version 5.3.7.7 bos.acct Version 5.3.7.8 bos.adt.base Version 5.3.7.3
bos.adt.debug Version 5.3.7.3 bos.adt.include Version 5.3.7.7 bos.adt.insttools Version
5.3.7.2
...
perfagent.tools Version 5.3.7.4 printers.rte Version 5.3.7.2|OS Version 5300-07-01-0748,
Proxy http://192.168.100.184:80/, Update-URL www14.software.ibm.com/webapp/set2/fixgetWe are creating and testing the nagios plugin to let Nagios run the SSH command:
nagios@susie112:~> vi /srv/app/nagios/libexec/check_aix_patchlevel.sh
#/bin/sh
/usr/bin/ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i /srv/app/nagios/.ssh/nagios-key \
-l aixhost-user $1 "sudo /scripts/check-aix-update.pl"
nagios@susie112:~> /srv/app/nagios/libexec/check_aix_patchlevel.sh 192.168.245.129
WARNING - 210 update(s) available: X11.Dt.lib Version 5.3.7.2 X11.Dt.rte Version 5.3.7.3
X11.apps.rte Version 5.3.7.1 X11.base.lib Version 5.3.7.2 X11.base.rte Version 5.3.7.5
...
perfagent.tools Version 5.3.7.4 printers.rte Version 5.3.7.2|OS Version 5300-07-01-0748,
Proxy http://192.168.100.184:80/, Update-URL www14.software.ibm.com/webapp/set2/fixgetNagios service configuration
After creating the SSH plugin script, we add it to commands.cfg and create our AIX patch service configuration file.
susie112:~ # vi /srv/app/nagios/etc/objects/command.cfg
# 'define check_aix_patch'
define command{
command_name check_aix_patchlevel
command_line $USER1$/check_aix_patchlevel.sh $HOSTADDRESS$
}
nagios@susie112:~> vi /srv/app/nagios/etc/objects/aix-patch-services.cfg
###############################################################################
# Define a servicegroup for AIX patch service checks
# All AIX patch service checks will be members of this group
###############################################################################
define servicegroup{
servicegroup_name aix-patch-checks ; The name of the servicegroup
alias AIX Update Checks ; Long name of the group
}
###############################################################################
# Define the generic patch check service template
###############################################################################
define service{
name generic-patch-aix
active_checks_enabled 1
passive_checks_enabled 1
parallelize_check 1
obsess_over_service 1
check_freshness 0
notifications_enabled 1
event_handler_enabled 1
flap_detection_enabled 1
failure_prediction_enabled 1
process_perf_data 1
retain_status_information 1
retain_nonstatus_information 1
is_volatile 0
check_period 24x7
max_check_attempts 3
normal_check_interval 720 ; check only once every 12 hours
retry_check_interval 2
contact_groups aix-admins, security-team
notification_options u,w,r ; notify unknown, warn, recovery
notification_interval 1440 ; notify only once per day
notification_period 24x7
register 0
servicegroups aix-patch-checks
}
###############################################################################
# AIX Patch Update Check via SSH - AIXHOSTS 1-3
###############################################################################
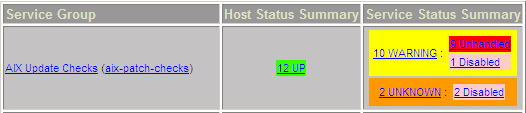
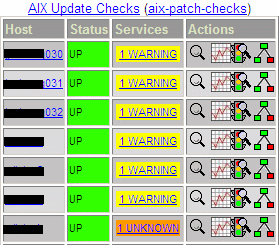
define service {
use generic-patch-aix
host_name aixserver1, aixserver2, aixserver3
service_description check_aix_patch
check_command check_aix_patchlevel
}Running the AIX patch check notification through SNMP traps
By setting up a passive check through SNMP traps, we avoid the security implications of configuring SSH user access to each AIX host. Instead, we need to change the check-aix-update.pl to send its data through a SNMP trap. AIX comes with the 'snmptrap' command, so instead of sending the update information to STDOUT, we call this trap program. The new plugin is named aix_update_trapsend.pl and it is configured to run on the AIX hosts once a day through cron. On the top of the perl script are the settings for the SNMP server and trap community to be used by 'snmptrap'. On the Nagios side, I needed to update /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf to accept and handle the AIX patch update traps. I also needed to update to the Nagios traphandler program send_trap_data.pl with a new filter that is processing, formatting and injecting the new AIX patch trap messages into Nagios.
Plugin Design with SNMP Traps
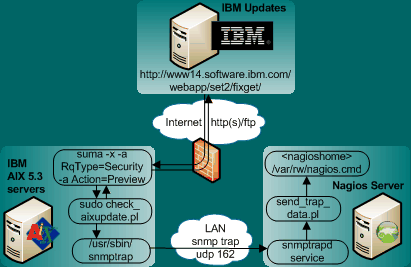
susie112:/ # vi /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf
# capture cron-scheduled patch update notification from AIX:
# SNMPv2-MIB::snmpTrapOID.0 = RFC1155-SMI::enterprises.2.0.1
traphandle RFC1155-SMI::enterprises.2.0.1 /srv/app/nagios/libexec/send_trap_data.plNagios configuration with SNMP trap setup
Here the Nagios configuration for the same AIX patch check configured as SNMP trap:
nagios@susie112:~> vi /srv/app/nagios/etc/objects/aix-patch-services.cfg
###############################################################################
# Define the aix patch trap service template
###############################################################################
define service{
name generic-patch-aixtrap
active_checks_enabled 0 ; traps are only passive checks
passive_checks_enabled 1 ; yes, check passive
parallelize_check 1 ; yes, please
obsess_over_service 0 ; we don't run extra commands
check_freshness 1 ; check if a report came in
freshness_threshold 93600 ; 26 hour threshold, since
; check runs only once a day
check_command no-patch-report ; this command is run only if
; service results are "stale"
notifications_enabled 1 ; send notifications
event_handler_enabled 1 ; yes, but we have none
flap_detection_enabled 0 ; with daily updates, no need
failure_prediction_enabled 1 ; dependency checks
process_perf_data 0 ; don't send this to perfdata
retain_status_information 1 ; yes, we keep it
retain_nonstatus_information 1
is_volatile 1 ; enable for passive checks
check_period 24x7 ; always check for submissions
max_check_attempts 1 ; one trap is enough
normal_check_interval 1
retry_check_interval 1
contact_groups aix-admins, security-team
notification_options w,r ; notify warnings and recovery
notification_interval 1440 ; notify once a day
notification_period 24x7 ; always notify
register 0 ; template, don't register
servicegroups aix-patch-checks
}
###############################################################################
# Receive SNMP traps for AIX update notifications from hosts withouth SSH
###############################################################################
define service {
use generic-patch-aixtrap
host_name aixserver1, aixserver2, aixserver3
service_description check_aix_patchtrap
}Comments
- Instead of using SSH for active remote checks, we could also deploy 'agent' software, a remote daemon that is executing these checks, however the effort of a agent installation is harder to get done unless the server owners can be convinced.
- The plugin script check-aix-update.pl checks the output of 'suma' against the list of installed software returned by lslpp, and lists only the software that belongs to the current TL of AIX. Suma itself checks already for applicable patches against the inventory and returns a couple of more package updates then I expected:
AIXTHOST3@[/home/myuser]> sudo /usr/sbin/suma -x -a RqType=Security -a Action=Preview \
| grep -v 5.3.7
Password:
****************************************
Performing preview download.
****************************************
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/devices.chrp.base.ServiceRM.1.3.0.72.bff
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/invscout.rte.2.2.0.12.bff
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/perl.rte.5.8.2.71.bff
Download SUCCEEDED: /usr/sys/inst.images/installp/ppc/radius.base.rte.2.1.7.1.bffI could not verify yet why these IBM package versions differ from the typical AIX level numbering (i.e. 5.3.TL.SP) and if it is OK to simply include them in normal patch notifications. If you happen to know more, please drop me a line - public [at] frank4dd [dot] com. I would be happy to simply trust 'suma' and avoid the additional check against 'lslpp'-reported inventory.
Credits, copyrights original scripts and links
- The script check-aix-update.pl can be found here check-aix-update.pl v1.0
- The script aix_update_trapsend.pl can be found here aix_update_trapsend.pl v1.0
- The latest update of send_trap_data.pl can be found here send_trap_data.pl v1.2
- Nagios and the Nagios community can be found at http://www.nagios.org/
- Information about AIX "Service Update Management Assistant" 'suma' can be found at http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/aix/library/au-updateaix.html
- SUSE Linux and SLES10 are products and trademarks of Novell, Inc. http://www.suse.com/
- AIX is a product and trademark of International Business Machines Corp. http://www.ibm.com/
- Further Nagios documentation is available here http://nagios.fm4dd.com/docs/en/